Retirement Ages
In the EU Member States, the most general retirement age is 65 years. Spain, Germany and France are about to raise their retirement age from 65 to 67 years, while the goal is 68 years in Britain and Ireland.
Increasingly, the retirement age is being linked to life expectancy. In addition to Finland this mechanism is available in Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, Greece, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal and Slovakia. Also in Britain, after mechanical increases, the retirement age will rise taking life expectancy into account.
For the main part, the changes in retirement ages are scheduled to take place between 2020 and 2030.
In some countries, the retirement ages are different for men and women. In that case, women have a lower retirement age. As a rule, as the retirement ages rise, women’s retirement ages will be the same as those of men.
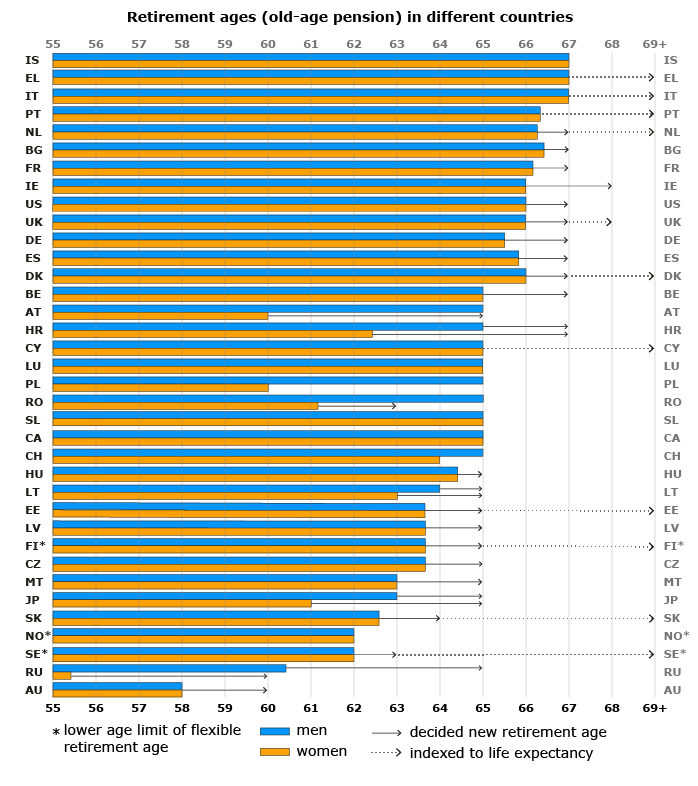
Current retirement ages (2020)
Check out the retirement ages and decisions to raise the retirement ages in the table of comparison below. The table lists first the earnings-related retirement age, then the national retirement age if it deviates from the first. Men’s and women’s retirement ages are also listed, if they differ from each other.
The retirement ages in the table are the earliest ages at which a person can withdraw a statutory pension without deductions for early retirement. In most cases, people can also retire late. As a rule, they are entitled to an increment for late retirement.
In many countries it is possible to retire early, before the general retirement age of the old-age pension. In some countries, if the insurance period is long, the pension taken into payment early is not reduced. These special arrangement have not been included in the table.
The retirement age in Norway, Sweden and Finland is flexible. That means that a person can take out their pension within a certain age range. The upper and lower age limits have been listed in the table.
| Current general retirement age (2020) | Future retirement age | |
|---|---|---|
| EU | Men/ Women | Retirement age or men/women |
| Austria (AT) | 65 / 60 years | 65 years (2033) |
| Belgium (BE) | 65 years | 67 years (2030) |
| Bulgaria (BG) | 66 years and 6 months | 67 years (2023) |
| Croatia (HR) | 65 / 62 years 6 months | 67 years (2038) / 65 years (2030); 67 years (2038) |
| Cyprus (CY) | 65 years | 65+ years (2023) |
| Czech (CZ) | 63 years and 8 months | 65 years (2036) |
| Denmark (DK) | 67 years; 66 years* | 67 years (2022); 68+ years (2030) |
| Estonia (EE) | 63 years and 9 months | 65 years (2026) 68+ (2027) |
| Finland (FI) | 63 years 9 months – 68 years; 65 years* | 65+ years (2027); 65+ (2030) |
| France (FR) | 66 years and 7 months | 67 years (2023) |
| Germany (DE) | 65 years and 8 months | 67 (2031) |
| Great Britain (GBR) | 65 years and 7–12 months | 67+ (2028), 68 (2046) |
| Greece (EL) | 67 years | 67+ years (2021) |
| Hungary (HU) | 64 years and 6 months | 65 years (2022) |
| Ireland (IE) | 66 years | 68 years (2028) |
| Italy (IT) | 67 years | 67+ years (2022) |
| Latvia (LV) | 63 years and 9 months | 65 years (2025) |
| Lithuania (LT) | 64 years / 63 years | 65 years (2026) |
| Luxembourg (LU) | 65 years | – |
| Malta (MT) | 63 years | 65 years (2027) |
| Netherlands (NL) | 66 years 4 months | 67+ years (2022) |
| Poland (PL) | 65 years / 60 years | – |
| Portugal (PT) | 66 years and 5 months | 66+ years (2016) |
| Romania (RO) | 65 years / 61 years 3 –5 months | -/63 years (2030) |
| Slovakia (SK) | 62 years and 6–8 months | 63 years and 2 months+ (2024) |
| Slovenia (SI) | 65 years | – |
| Spain (ES) | 65 years and 10 months | 67 years (2027) |
| Sweden (SE) | 62-68 years; 65 years* | 63-69 (2023), 63+ (2026); 66 (2023), 66+ (2026) |
| Other countries | Men / Women | Retirement age or men/women |
| Australia | 58 years; 66 years* | 60 years (2024); 67 years (2023)* |
| Canada (CA) | 65 years | – |
| Iceland (IS) | 67 years | |
| Japan (JP) | 63 years / 61 years; 65* | 65 years (2025) / 65 years (2030); – |
| Norway (NO) | 62–75 years; 67 years* | – |
| Russia (RU) | 60 years and 6 months / 55 years and 6 months | 65 years (2028); 60 (2028) |
| Switzerland (CH) | 65 years / 64 years | – |
| USA (US) | 66 years | 67 years (2027) |
| * FI, SE, DK, NO, AU and JP: the retirement age of the earnings-related pension has been separated from that of the national pension with a semicolon. | GP= Government proposal or plan of equivalent administrative level | + = Retirement age rising along with the increasing life expectancy. |
NL: The retirement age will rise by 3 months/year until it is 67 years in 2024. After that, it will be linked to changes in life expectancy.
BE: The retirement age will rise to 66 years in February 2025 and 67 years in February 2030. It is possible to retire earlier if one’s working life has been long.
UK: The retirement age will rise to 67 years by 2028, after which it will be linked to life expectancy. According to the current schedule, the retirement age will rise to 68 years by 2046.
BG: The retirement age will rise by 2 months/year until it is 67 years in 2023. After at least 35 years and 10 months of insured work (women) or 38 years (men), a person can retire earlier.
ES: If a person has worked for more than 37 years, the retirement age is 65 years. In 2027, the requirement will rise to 38.5 years.
IE: The retirement age will rise to 67 years by 2021 and 68 years by 2028.
IT: The retirement age is linked to life expectancy.
AT: Women’s retirement age will be raised gradually (6 months/year) to 65 years from 2024 to 2033. Persons with a long working life can retire earlier.
EL: The retirement age will be linked to life expectancy in 2021. If the working life spans at least 40 years, it is possible to retire at age 62.
HR: Women’s retirement age will rise by 4 months/year until it is 65 years in 2027. After that, both men’s and women’s retirement age will rise by 4 months/year until it is 67 years in 2033.
CY: The retirement age is determined based on changes to life expectancy over a period of five years. Under certain conditions, people can retire on an old-age pension already at age 63.
LV: The retirement age will rise by 3 months/year until it is 65 years in 2025.
LT: The retirement age for men will rise by 2 months/year and for women by 4 months/year until the retirement age for men and women is 65 years in 2025.
MT: After a long insurance period (35 years), it is possible to retire at age 61.
PT: The retirement age is determined based on the change in life expectancy for the 65-year-olds.
FR: The pension can be drawn without reductions at 62 years in case of a full insurance period (41 years and 6 months). It is possible to take payment of a reduced pension before reaching the retirement age.
RO: Women’s retirement age will rise by one month every 3 months until 2023. After that, by 1 month/5 months until it is 63 years in 2030.
SE: Flexible retirement age (62-68 years) for earnings-related pensions; guaranteed pension 65 years. The retirement age for the guaranteed pension will rise to 66 years (2023); the earnings-related retirement age 62-68 (2020), 63-69 (2023). Both retirement ages will be linked to changes in life expectancy as of 2026.
DE: The general retirement age (Regelaltersgrenze) will rise by 1 month/year until 2023 and by 2 months/year until it is 67 years. After a long insurance period, the pension can be granted around 2 years before the general retirement age.
SK: The retirement age is rising by 2 months/age cohort until it is 64 years in 2023. According to a currently valid decision, the retirement ages will not rise above 64 years.
SI: Women can be granted a pension at age 64 years and 6 months if they have been insured for more than 20 years. In addition, a pension can be granted to both men and women at age 60 if they have been insured for at least 40 years. Having children lowers the retirement age of women by a maximum of 4 years (for 5 or more children). The mandatory military service lowers the retirement age of men by 2 years at the most.
FI: Flexible retirement age: 63 years and 9 months–68 years, national pension 65 years. The earnings-related retirement rises by 3 months/year until it is 65 years in 2027. In 2030, the retirement age will be linked to life expectancy.
DK: National retirement age: 65 years. ATP retirement age: 67 years. The national pension retirement age will rise to 67 years in 2019-2022. As of 2030, the retirement age will be linked to life expectancy.
CZ: The retirement age will rise for men by around 2 monhts/year and slightly faster for women, until it is 65 years for both genders in 2030. Special rules for mothers until 2036. After 2030 the aim is to raise the retirement age so that the time spent in retirement would be a quarter of one’s lifespan. The changes in life expectancy are monitored every five years.
HU: The retirement age will rise by 6 months/year until 2022, when it will be 65 years. Women can retire at any age providing they have been insured for at least 40 years (or less, if they have 5 or more children).
EE: The retirement ages will rise by 3 months/age cohort (for those born between 1954 and 1960). For those born in 1961 or later, the retirement age is 65 years (in 2026). As of 2027, the retirement age will be linked to changes in life expectancy. Having children may reduce the retirement age by 3-5 years.
AU: The retirement age of the mandatory insurance (Superannuation) will rise by 12 months/year until it is 60 years in 2025. The retirement age of the minimum pension (Age pension) will rise by 6 months/two years until it is 67 years in 2023.
IS: The government has withdrawn its bill which would have raised the retirement age gradually to 70 years by 2041.
JP: The retirement age of the national pension (without reductions) is 65 years. The retirement age of the earnings-related pension will rise for men to 65 years by 2025 and for women to 65 years by 2030.
CA: Retirement age of the old-age pension (without reductions). Flexible retirement age for the earnings-related pension: 60-70 years, and for the national pension 65-70 years.
NO: Flexible retirement age: 62-75 years. Regular retirement age: 67 years. The pension must be high enough to be allowed to retire under the age of 67.
RU: After a long working life, a certain number of children, professions that are defined strenuous, and for workers in the northern parts of the country, it may be possible to retire earlier.
US: The retirement age will rise by 2 months/year as of 2021.